MIAMI (Reuters) — A slightly below-average 2023 Atlantic hurricane season lies ahead with an El Nino weather phenomenon damping the storm outlook, a top hurricane forecaster said.
El Nino, a weather system that forms from warm ocean surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific, increases vertical wind shear, lessening or breaking up tropical storms.
“If a robust El Niño does not develop, the potential for an active Atlantic hurricane season still exists,” according to the first outlook by Colorado State University researchers.
The forecasters expect two major hurricanes, or those with wind speeds of at least 111 miles per hour (179 kph), to develop out of six hurricanes and 13 named storms.
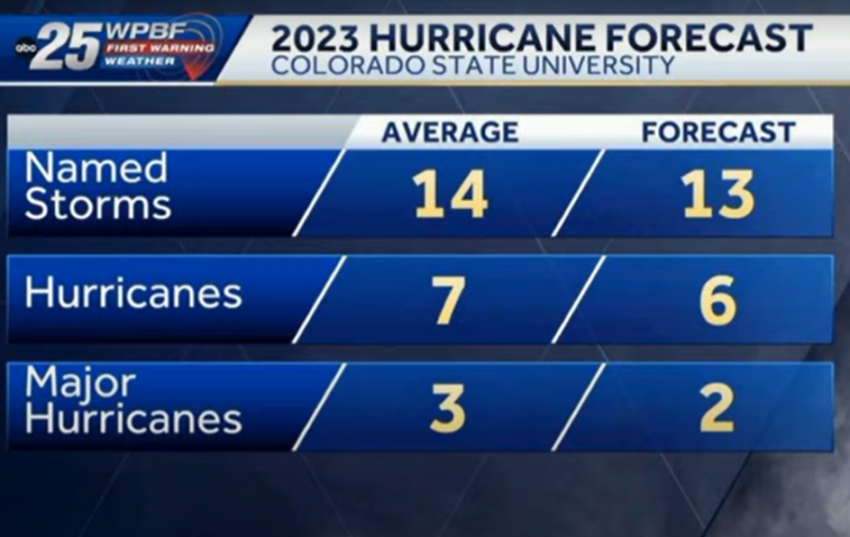
An average Atlantic season has 14 named storms, seven hurricanes and three major hurricanes.
Last year broke a six-year string of above-normal hurricane seasons. CSU had estimated four major hurricanes but only two developed, including Hurricane Ian that spawned 150 mph winds, and hit Florida and South Carolina.
This year’s storms have a higher chance of striking the Gulf Coast of the United States rather than the Atlantic coast. CSU sees a 28% chance for a Gulf Coast hit and a 22% chance for strikes to the Atlantic coast, forecasters said.
Overall, there is a 44% chance for a strike along the continental United States coastline and a 49% chance a major hurricane will move through the Caribbean, Colorado State said.
Phil Klotzbach, who leads Colorado State’s Tropical Meteorology forecasters, said on Thursday that without the expected El Nino development, warm ocean temperatures in the eastern Atlantic would shape the Atlantic hurricane season that begins on June 1.
“Our forecast is really bullish and that’s because of sea surface temperatures, especially in the eastern Atlantic,” Klotzbach said at the National Tropical Weather conference.
Warm waters in the eastern Atlantic provide an area for low pressure systems coming off the west African coast to begin developing into storms, Klotzbach said.
Reporting by Erwin Seba; Editing by Sandra Maler
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles.

